Images first and last: ©Sempergreen Services LLC.
Images others: ©Kate Joyce/Ross Barney Architects
Green walls: Sempergreen
Year: 2020
City: Orlando, Florida, USA
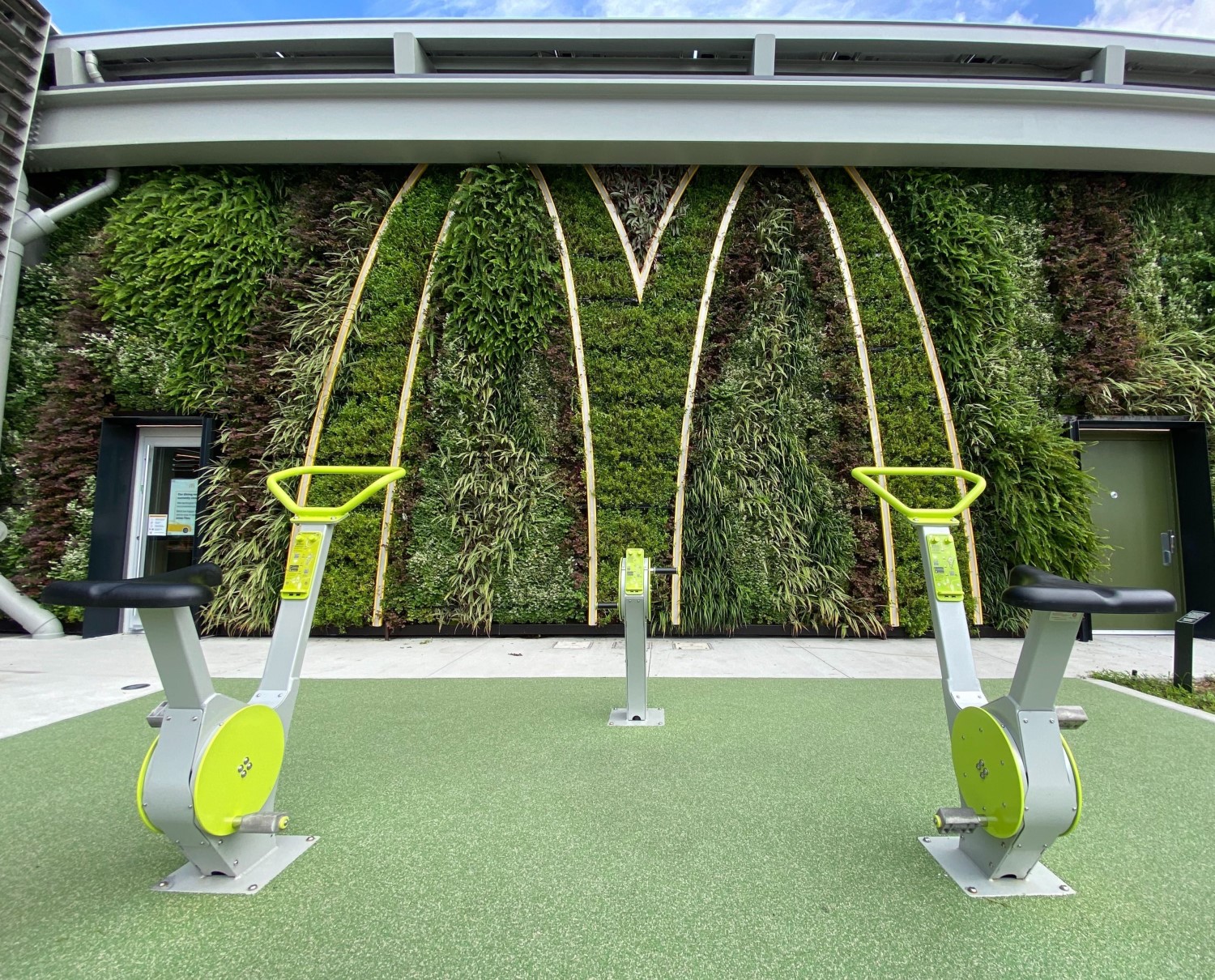
McDonald’s has opened a sustainable flagship restaurant at Walt Disney World in Orlando, Florida. With this pilot project, they’re aiming to have the first energy-neutral fast food restaurant in the world. The restaurant’s many eco-friendly features include two SemperGreenwalls covering almost 185 square meters.
The first energy-neutral fast food restaurant in the world

McDonald’s has opened a sustainable flagship restaurant at Walt Disney World in Orlando, Florida. With this pilot project, they’re aiming to have the first energy-neutral fast food restaurant in the world. The restaurant’s many eco-friendly features include two SemperGreenwalls covering almost 185 square meters.
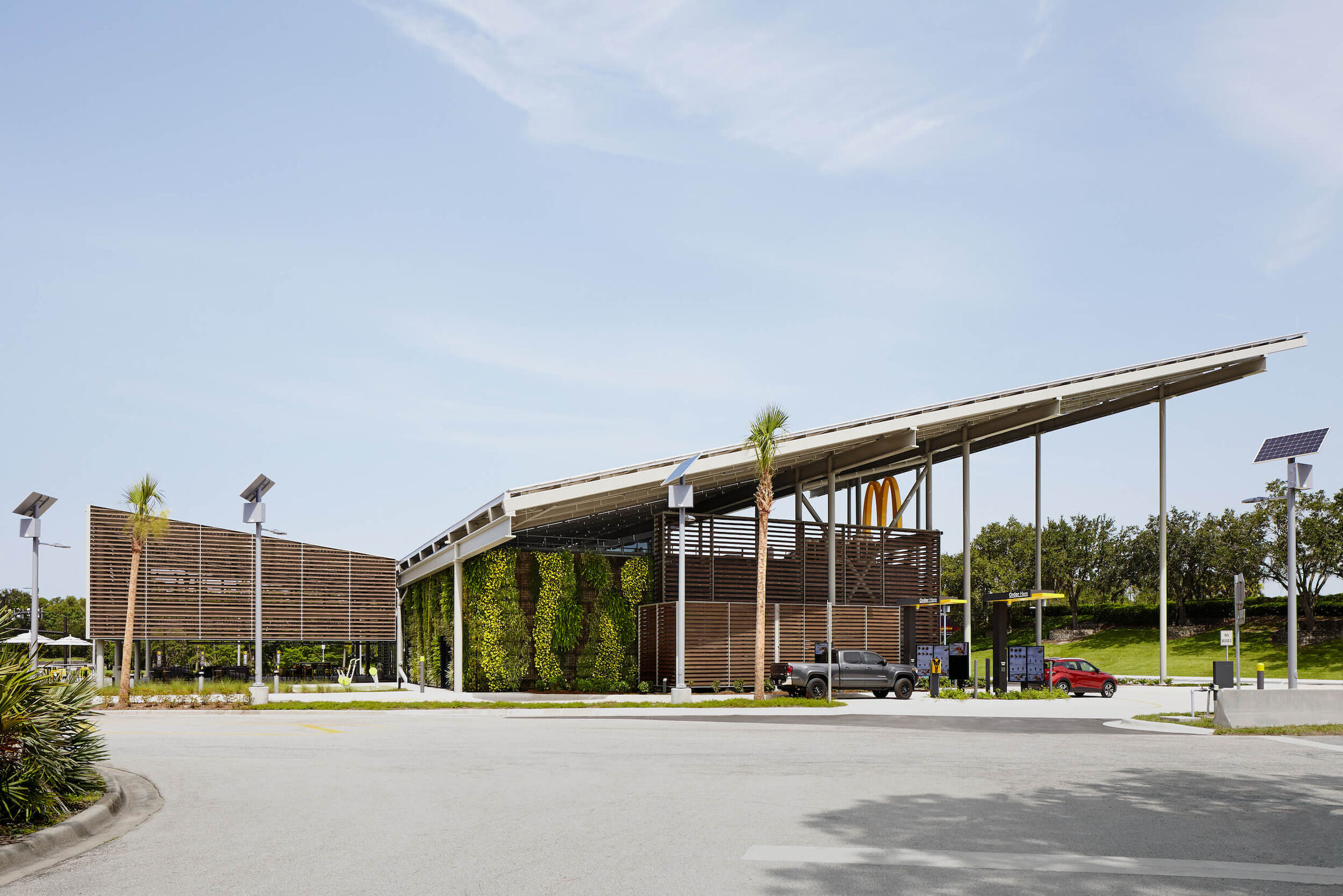
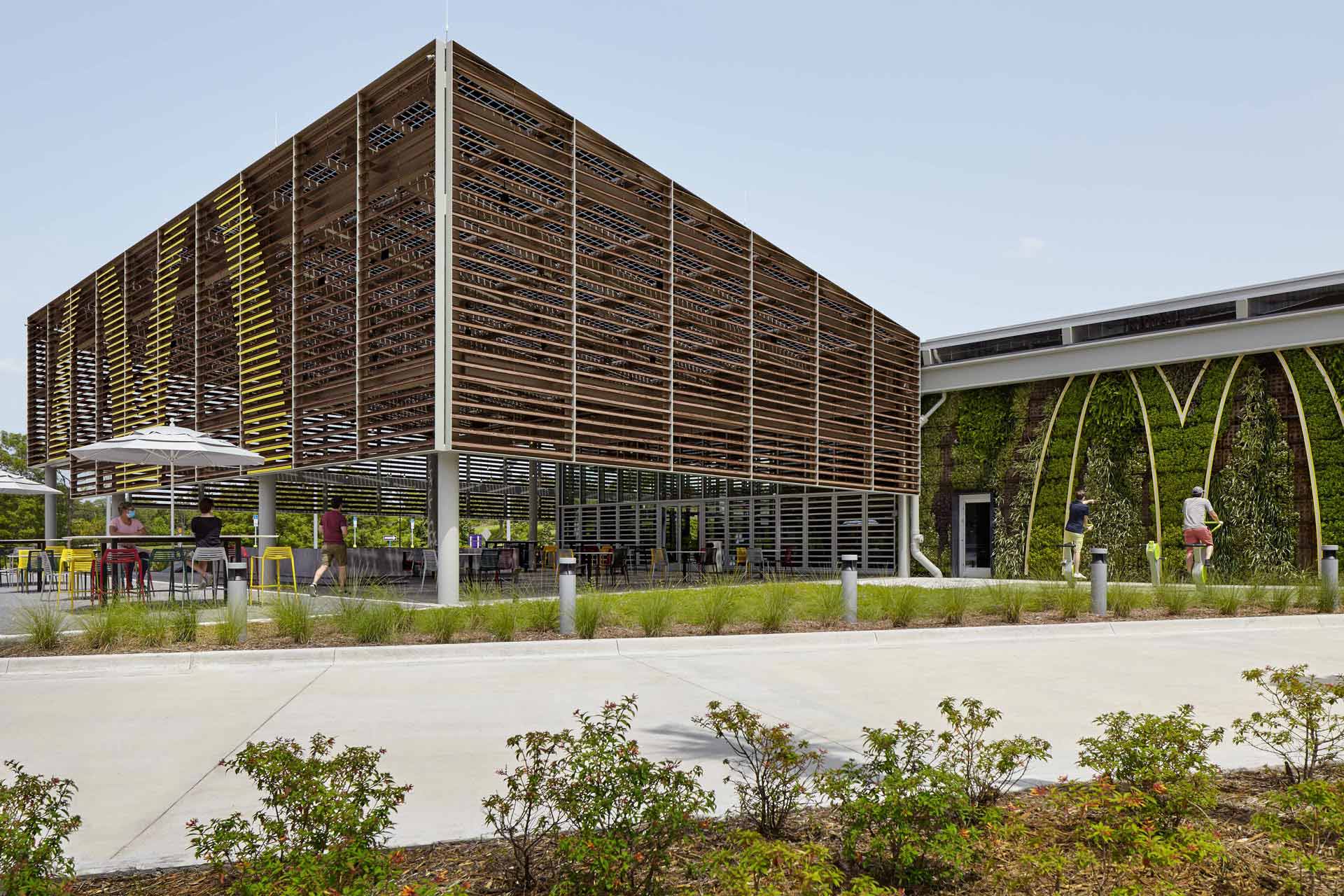
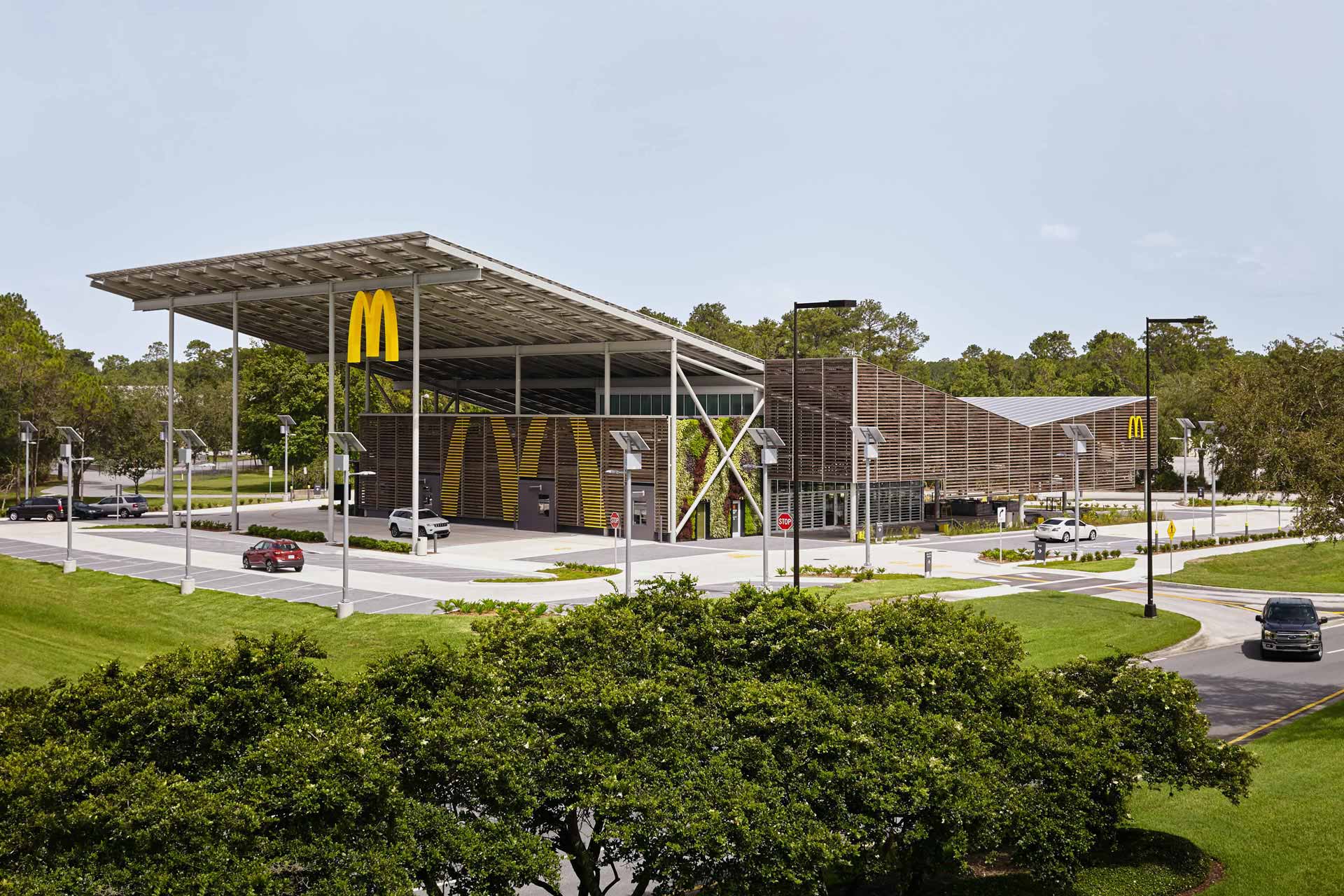
The restaurant has been designed by Ross Barney Architects and architectural and engineering firm CPH. Not only were the living walls included as an impressive design feature, they also offer environmental benefits like reducing water runoff, cooling the air in- and outside the building, and stimulating local biodiversity.
Green living walls year-round
The designers have also been involved in the plant choices for the SemperGreenwalls. These have been tailored to the subtropical climate of Orlando, including native Floridian plants that require less water. To keep the facades green all year round, they have been equipped with the unique Sempergreen Plant Care System. This web-based system allows the walls to be monitored remotely and ensures that the plants are provided with the correct amount of water and nutrients.
Sustainability measures McDonald’s Flagship
The building also contains plenty of other environmentally-friendly features. On the roof, over a 1.000 solar panels and solar glass have been installed to run the whole restaurant on sustainable energy. At the ground level, permeable paving has been used to enable better water management on-site. The data and experiences from this pilot restaurant in Walt Disney World Orlando will be a source of information for McDonald’s global sustainability efforts.
Besides working towards their goal of lowering their CO2 emissions by 36% between 2015 and 2030, the fast food chain also wants to inform its customers about the importance of sustainability. Therefore, the restaurant offers fun green amenities, like informative games and bikes which customers can use to generate electricity and light up the McDonald’s logo. The lit arches of the ‘M’ create a beautiful contrast with the green walls surrounding them.
Architects/Designers: Ross Barney Architects and CPHN
Green walls on property: 2 green walls, 185 square meters
Green wall system: SemperGreenwall Outdoor